Cryptocurrencies : Definition
When you think of cryptocurrenciesAlthough we often think of Bitcoin, it's just one of the many types of cryptocurrency on the market. But what is a cryptocurrency?
It's a decentralized digital currency that works with a technology called blockchain. In short, a cryptocurrency is an entirely digital currency that is not issued by a central bank.
Each transaction is recorded in a public register (the blockchain). Its security is ensured by cryptography. These currencies enable direct exchange between people without going through an intermediary like a traditional bank. But this also means that controlling them can be complicated.
Why use cryptocurrencies?
High risk high reward
Independence from a traditional banking structure gives cryptocurrencies greater autonomy. Currencies of this type are always available. These currencies offer a return highEven so, it's not without its risks. Indeed, the value of cryptocurrencies can fall or rise very quickly and dramatically.
Enhanced safety
The blockchain public registry makes it possible to keep a trace of every transaction, forever. A transaction cannot be falsified, modified or deleted once it has been carried out. The register is not stored on a single computer, making it virtually impossible for a hacker to gain access.
Inclusiveness and availability
Unlike traditional banks, the cryptocurrency market remains open around the clock, always offering the opportunity to profit, even during the night hours. All you need is a connection internet to access it.
Disadvantages of cryptocurrencies
Extreme instability
We can't talk about cryptocurrencies without mentioning the risks high associated with them. Indeed, this type of investment has its share of risks, not least because of the instability of these currencies. Indeed, the value of a cryptocurrency can rise or fall drastically and rapidly.
The novelty and its drawbacks
While cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin can provide high returns in the short term, the viability of these currencies over the long term is more than uncertain. In fact, crypto-currencies are very new and have yet to prove themselves as a long-term investment.
As with other recent innovations such as AI, the novelty of this type of currency also means that regulations and laws concerning them are not yet fully developed, which can lead to abuse.
Swiss tax rules on cryptocurrencies
Payment tokens
Cryptocurrencies used as means of payment (also known as "payment tokens"), such as Bitcoin, are considered to be part of private wealth, in the same way as shares and bank accounts.
Cryptocurrencies used as a means of payment are not subject to withholding tax or stamp duty. However, you will need to mention these cryptocurrencies each year on your tax return, mentioning their value :
- Market value, if known (= what it's worth at the time)
- The value it had at the time of purchase if there is no official value (converted into Swiss francs)
If you don't generate any income from your tokens, you won't normally be taxed on your income. However, if you receive a salary or bonus in crypto, this is seen as income and you will therefore be taxed.
If you make a lot of transactions or if the amounts exchanged are high, this could be seen as a professional activity and you will therefore be taxed on the earnings. If you mine (create cryptocurrencies), this will also be considered taxable income, as in the case of self-employment.
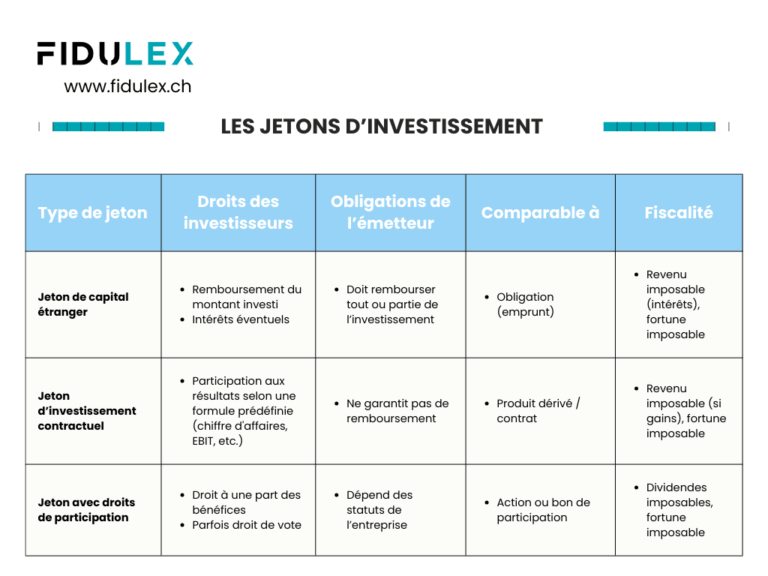
Investment tokens
The situation is much more complex for investment tokens. It is a good idea to check your personal case and compare it with the others. official information from the Confederation. Investment tokens are cryptocurrencies that give financial rights to the investor (for example: a refund, a share of profits, interest, etc.).
The tax treatment of these tokens depends on the type of contractual link between the investor and the issuer (the person or company who created the token). Each type of right must be analyzed separately for tax purposes.
Tax deductions
Fees related to the management of cryptos (such as portfolio or security fees) can be deducted. However, buying, selling or transfer fees are not deductible.





