- Since January 1, 2025, the minimum wage in Geneva has been CHF 24.48 per hour.
Minimum wage in Geneva: the essentials
Why this law?
This law was introduced to limit precariousness in workers in Geneva, as well as to guarantee all workers a decent income in line with the cost of living (with a few exceptions).
It also helps combat wage dumpinga practice of lowering salaries below those normally paid. Geneva now has one of the highest minimum wages not only in Swiss cantons, but also in the world.
Who is affected by this law?
This law applies to almost all economic sectors (with the exception of agriculture and horticulture, which are governed by other regulations).
In Geneva, the law is different for employment contracts such as:
- Apprenticeship contracts (e.g. CFC in a company)
- Internship contracts (e.g. university internships)
- Au-pair contract for under-18s
Other cantons, such as Basel City, have also increased the minimum wage, albeit to a lower level: CHF 21.70 per hour.
Evolution
History of AVS determinants salaries in force in the canton of Geneva from January 2020 to January 2024.
- Hourly rate
- Year
- CHF 23.- / hour
- CHF 23.14 / hour
- CHF 23.27 / hour
- CHF 24.- / hour
- CHF 24.32 / hour
- CHF 24.48 / hour
- 1.11.2020
- 1.01.2021
- 1.01.2022
- 1.01.2023
- 1.01.2024
- 1.01.2025
Changes in Geneva's minimum gross hourly wage since its introduction in November 2020
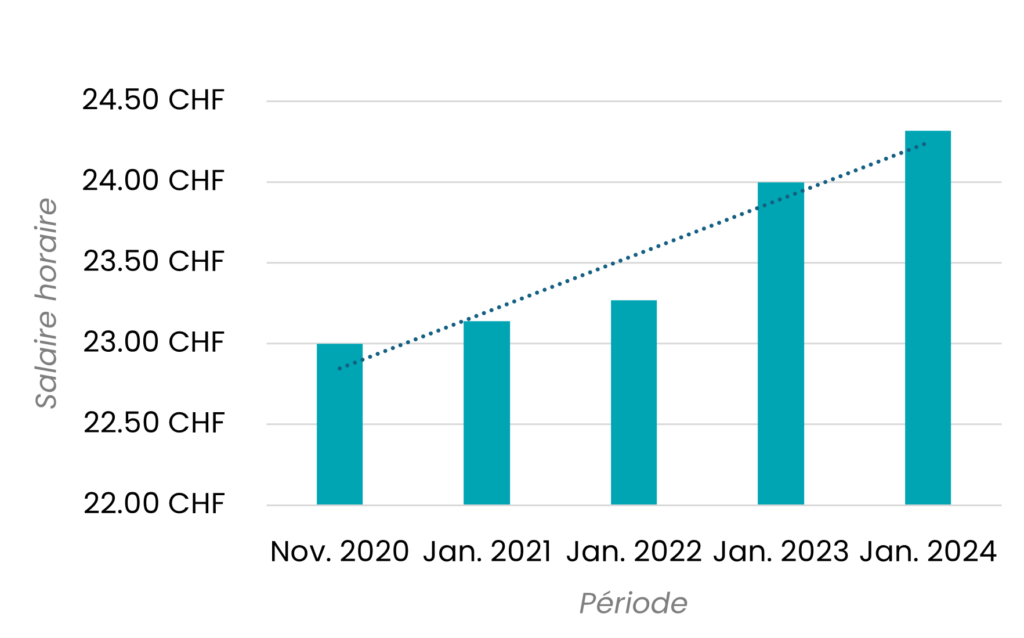
Data source: Minimum wage in the canton of Geneva, ge.ch
Evolution of the minimum gross monthly wage in Geneva [40h per week], since its introduction in November 2020
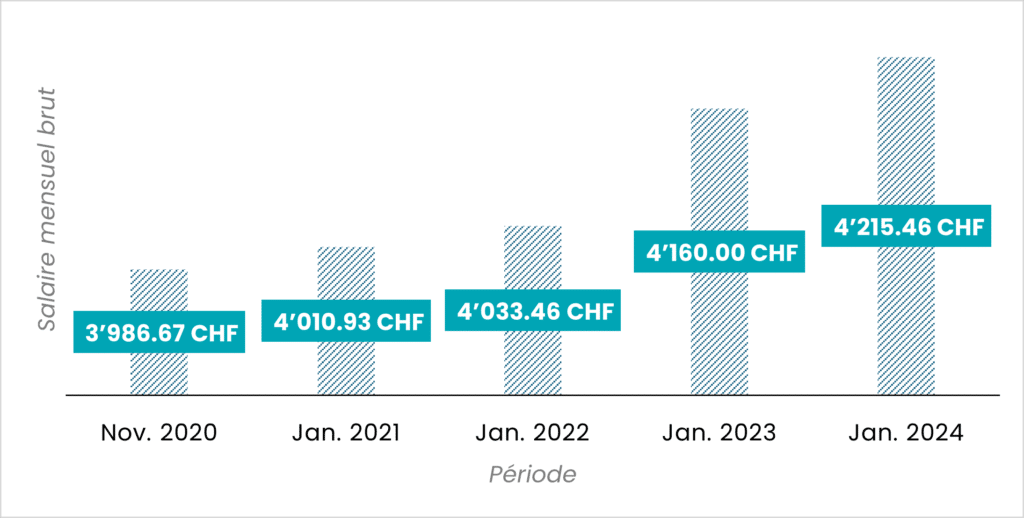
Data source: Minimum wage in the canton of Geneva, ge.ch
These two graphs show an exponential growth in the minimum wage, adjusting to the canton's cost of living from year to year. The data collected show a positive trajectory: in 2020, the minimum hourly wage was set at CHF 23 per hour, with a first increase of +0.61% the January 1, 2021. By 2024, the cumulative increase of 5.74% compared with 2020, reflecting a growing improvement in working conditions in Geneva.
Comparison of minimum wages in Switzerland in 2024
There is no minimum wage in Switzerland. However, some cantons have decided to adopt them. It should be noted that some CLAs may provide for a higher minimum wage, which will take precedence over that of the canton (see next section).
- Canton
- Hourly rate
- Neuchâtel
- Basel-Stadt
- Jura
- Geneva
- Ticino
- CHF 21.09 / hour
- CHF 21.70 / hour
- CHF 20.60 / hour
- CHF 24.32 / hour
- CHF 19.75 / hour
Minimum wage or collective bargaining agreement?
The Collective labor agreements (CLAs) govern the basic wages of a company or economic sector.
In principle, CLAs cannot set a lower wage than that in force in the canton (a CLA serves to protect employees and regulate working conditions between the two parties).
According to certain collective bargaining agreements, your salary must correspond to a certain amount, which may be above the minimum wage, depending on your profile.
Calculating Geneva's minimum wage
AVS determining salary
The minimum wage is defined as the AVS (old-age and survivors' insurance) determining wage. It is made up of all amounts subject to AHV.
Hourly-paid staff
For hourly-paid staff, such as domestic staff, vacation and public holidays must be included in the hourly wage (except in cases governed by a collective bargaining agreement). The minimum wage for an hourly-paid employee is calculated by multiplying the number of hours worked per week by the gross hourly wage minimum.
Sample Calculation
Here's a practical example of how to calculate the salary of a person working 42 hours a week.
- Hours worked
- Hourly rate
- Year
- 42 h / week
- CHF 24.- / hour
- 1.01.2023
Formula for calculating gross monthly salary : Minimum hourly wage x Number of hours worked x (52/12) = Minimum monthly wage
24 x 42 x (52/12) = a CHF 4'368.-
Compliance with current legislation
What happens if this new law is not respected?
In the event of non-compliance, theOffice Cantonal de l'Inspection et des Relations du Travail (OCIRT) provides for various penalties.
- Administrative fine of up to CHF 30,000
- Retroactive payment of unpaid wages
- Exclusion from public contracts (subject to conditions)
What can I do if I'm not paid properly?
OCIRT is the body responsible for ensuring compliance with working conditions in Geneva. The first thing to do is to contact them and explain your situation.
Alternatively, you can contact trade unions such as UNIA. This is particularly advisable if you are subject to a collective bargaining agreement.
Opposition to this law
From an economic point of view
Those opposed to the new law argue that it could createinflation. It would make companies less competitive and increase unemployment.
Higher wages could also lead to higher prices for consumers.
On the other hand, those in favor of this law claim that it could help increase the purchasing power of residents, while stimulating growth of a country.
This new wage law could therefore help reduce poverty and income inequality, which in turn could boost an economy's productivity.
Recourse
In 2020, several Geneva employers' associations lodged an appeal against the introduction of a minimum wage in the canton, amounting to CHF 23/hour.
The Fédération des entreprises romandes (FER) Genève argued that this measure could harm the local economy, particularly in the context of the post COVID-19 crisis. The appeal, which was lodged with the Constitutional Chamber of the Court of Justice, highlighted companies' fears about their competitiveness.¹
Median salaries in Geneva in 2020²
- Training
- Men
- Woman
- Without full training
- In-house training
- Apprenticeship (CFC)
- Maturité (professional or high school diploma)
- Teaching certificate
- Vocational training Sup.
- Advanced vocational school
- Colleges & Universities
- CHF 5,561
- CHF 5,864
- CHF 6,609
- CHF 7,483
- CHF 7,286
- CHF 8,972
- CHF 9,610
- CHF 12,083
- CHF 4,873
- CHF 5,758
- CHF 6,472
- CHF 7'438
- CHF 6,890
- CHF 8'410
- CHF 8,333
- CHF 10,038
¹ Radio Lac. (2020, October 6). Geneva: employers appeal against minimum wage. Radio Lac. Retrieved from https://www.radiolac.ch/actualite/geneve-les-patrons-recourent-contre-le-salaire-minimum/
² Cantonal Statistical Office (Date of publication). Chart or page title. Republic and Canton of Geneva. Retrieved from https://statistique.ge.ch







