- Wealth tax is levied on net wealth
- Wealth tax is progressive
- Each Swiss canton applies its own tax rate
- Listed securities are valued at their December 31 value.
Wealth Tax: What Is It?
Wealth tax in Switzerland is a direct tax levied on the total value of an individual's personal property and assets. The tax is calculated on the net wealth of the taxpayer, i.e. all assets, not including debts.
Unlike the income tax, which is based on a person's income over the course of a year, the wealth tax focuses on accumulated wealth. The wealth tax is also typically lower than income tax .
Wealth tax is levied solely by the canton of residence or by the location of a property. This competence is entrusted to the cantons by the confederation and codified by the art. 2 of the LHID.
Taxable Wealth
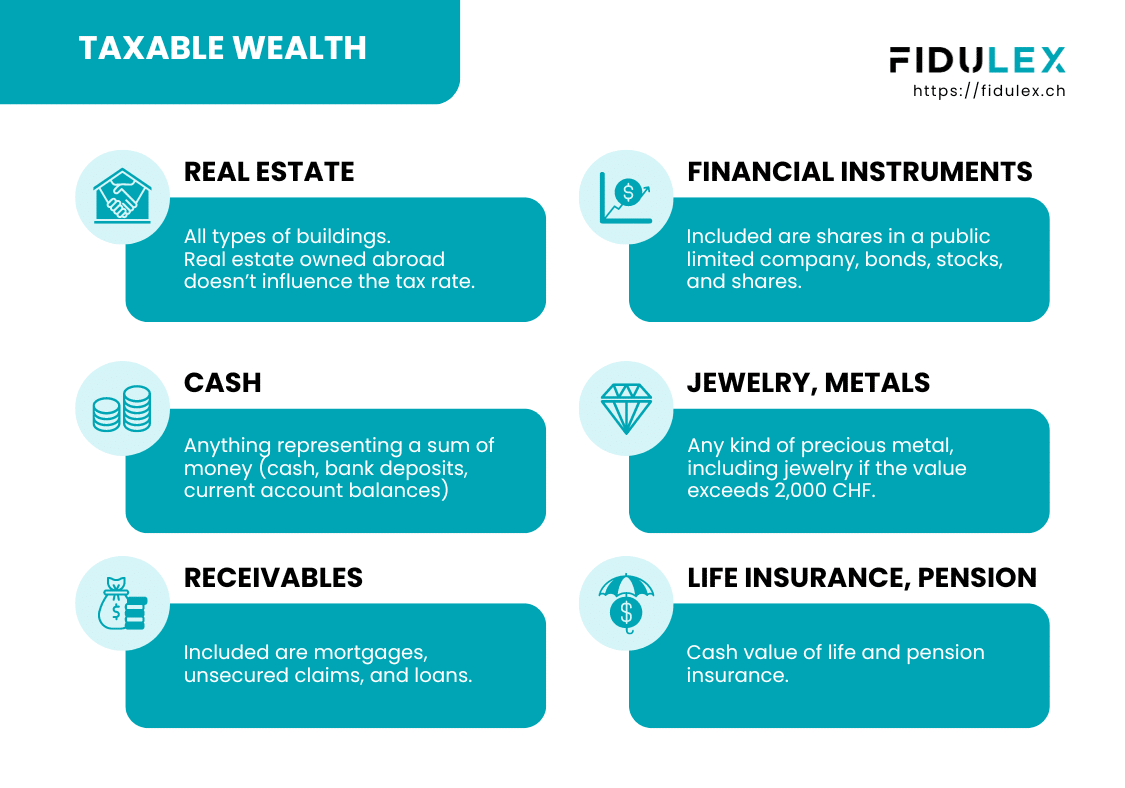
Here is a non-exhaustive list of the various items subject to wealth tax, and which must therefore appear in the tax return. These may vary from canton to canton.
- Real estate : All types of building.
It should also be noted that real estate owned abroad does not influence the tax rate, although it must be declared.
However, please check that the country where you own your property has a double taxation agreement with Switzerland. France, for example, has a double taxation agreement with Switzerland.
- Financial instruments : Included in this category are items such as shares in a public limited company, bonds, securities and interests in companies, societies or associations.
- Cash and bank deposits : This refers to any security representing a sum of money. Examples include cash, bank deposits and current account balances.
- Units in collective investments with direct real estate : The difference between the total value of the investment's assets and the value of its real estate.
- Receivables : Both mortgage and unsecured claims.
- Business assets : All components of business assets.
- Life insurance and pensions : We're talking here about the cash surrender value of life and pension insurance.
- Jewelry and silverware : The latter are included in this category only if their value exceeds CHF 2,000.
- Precious metals : Gold, silver or platinum, for example.
- Livestock : This includes both dead and live cattle.
Non-Taxable Wealth
- Furniture and Collections : Furniture, including artistic and scientific collections that can be considered as such.
- Clothing : All types of clothing.
- Household utensils : The various tools used in the household.
- Books : Books for the personal use of the taxpayer and his family.
- Retirement savings (LPP) : The capital paid in for occupational pension savings (BVG).
Estimation of Items Subject to Wealth Tax
Moveable Assets
- Cryptocurrencies
- Cash
For tax purposes, you will need to provide a bank statement showing balance as at December 31.
- Listed securities
- Unlisted securities in Switzerland
This is based on yield and intrinsic value. The special rules for real estate companies are in accordance with CSI Circular No. 28.
- Foreign unlisted securities
The treatment is similar to Swiss non-listed securities. Detailed financial documents will be required, with an option for Tax Ruling.
- Loans granted
- Commercial securities
- Life insurance
- Jewelry and silverware
Such assets will be valued at resale value under normal market conditions.
Real Estate Assets
- Buildings
The tax value is based on the purchase price indicated in the contract. It is taxable to the owner if subject to usufruct.
- Real estate abroad
The purchase price is converted into Swiss francs using the tax rate for the year of acquisition. It is included only to determine tax rate.
- Real estate received (donation/succession)
The tax value established by the tax authorities at the time of the donation or inheritance.
- Commercial and/or industrial buildings
Valued according to the current value of the land, buildings and ancillary facilities.
- Farm buildings
Valued at their yield value, including the part used as housing for farming and forestry operations.
What debts and deductions are allowed?
Deductible debts include unsecured debts, mortgages, justified private debts and negative account balances.
Geographical breakdown of debt
In Switzerland, only proportional debts linked to taxable assets can be deducted, depending on their location.
Flat-rate deductions
In Switzerland, lump-sum deductions are established. This means that a taxpayer with assets below a defined amount won't pay any wealth tax.
- Geneva : CHF 82,200 for a single person and CHF 164,400 for a couple
- Vaud : CHF 58,000 for a single person and CHF 116,000 for a couple
- Valais : CHF 30,000 for a single person and CHF 60,000 for a couple
- Schwyz : CHF 125,000 for a single person and CHF 250,000 for a couple
Flat-rate deductions in Geneva
Other flat-rate deductions are available for self-employed people and partners in partnerships.
How do you determine the value of assets?
To determine the value of a property, you need to know the market value.
In the case of real estate, for example, unless it is used for agricultural activities, it will generally be valued at market value.
However, this value varies depending on the canton. Some use the market value to estimate the value of a property, while others use the yield value.
Wealth Tax by Canton
As with income tax, the cantons have free choice in setting wealth tax rates. Some cantons have decided to keep their tax rates moderate, while others a little higher but with other advantages.
Here's a list to give you an idea of how much cantonal and communal taxes amount for a single person without children. Tax amounts are in CHF.
| Township, city | 100k | 500k | 1 mio | 5 mio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GE - Geneva | 81 | 2 011 | 5 485 | 44 286 |
| VD - Vaud | 188 | 2 615 | 6 478 | 38 141 |
| SZ - Schwyz | 101 | 1 005 | 2 010 | 10 050 |
| ZG - Zug | 0 | 472 | 1 750 | 12 470 |
| ZH - Zürich | 49 | 694 | 2 118 | 24 242 |
| VS - Wallis | 284 | 2 205 | 5 127 | 31 345 |
| FR - Fribourg | 142 | 2 014 | 5 020 | 26 188 |
| NE - Neuchâtel | 286 | 3 420 | 6 840 | 34 200 |
| JU - Jura | 173 | 1 605 | 3 989 | 26 495 |
| BS - Basel | 28 | 2 298 | 6 050 | 39 626 |
| BE - Bern | 153 | 1 632 | 4 111 | 28 018 |
| NW - Nidwalden | 131 | 632 | 1 259 | 6 269 |
| UR - Uri | 70 | 848 | 1 823 | 9 623 |
Wealth tax rates by canton
Wealth tax in Geneva
Wealth taxation in Geneva begins once the flat-rate deduction applied. The basic wealth tax is calculated in brackets, with specific rates applied to each level of wealth.
The wealth bracket between CHF 1 and CHF 114,621 is taxed on 1.75‰. This gives a maximum tax of CHF 200.60 for this bracket.
For higher levels of wealth, rates gradually increase to 4.5‰ for assets exceeding CHF 1,719,304. Once the basic tax has been determined, a supplementary tax, as well as cantonal and municipal taxes, are added.
Wealth tax in the canton of Vaud
Wealth tax in the canton of Vaud is also calculated in brackets.
The lowest wealth bracket is taxed at a low rate. For a wealth of CHF 100,000, the rate is 0.779‰ with a basic tax of CHF 77.90.
While above CHF 2,000,000 of taxable wealth, the tax on the additional thousands is calculated at the rate of 3.39 ‰.
Wealth tax in Valais
In the Swiss canton of Valais, wealth tax is levied by the canton and the communes on a progressive scale.
For goods between CHF 1,000 and 200,000, the rate varies in increments of CHF 1,000, with a gradual increase of around 0.1 to 0.2 %.
Above CHF 1,901,000, tax rate reaches 3%.
Wealth tax in Schwyz
In Canton Schwyz, the wealth tax is 0.6‰ and applies in a linear way. This means that the rate remains the same regardless of the amount of wealth.
For real estate, the official value which serves as the basis for taxation.
Wealth tax in Zug
In Zug, the wealth tax for 2024 will vary between 0.425 and 1.9‰. Starting in 2024, discounted rates will apply and the tax will be progressive, with the rate increasing with wealth.
How to reduce wealth tax?
There aren't many options available for lowering the wealth tax rate, but there are a few ideas that can be implemented.
- You can compare and choose to settle in a canton with a lower tax rate, thus saving money.
- Another option would be to invest in real estate, as the taxable value of a property will generally be lower than its actual value.
- You can also transfer funds to tax-free assets such as 2nd and 3rd pillars, which will reduce your taxable assets.
Frequently Asked Questions
When does wealth tax liability begin and end?
Unlimited tax liability generally begins when a person takes up residence in Switzerland or starts a tax residence.
It ends with departure from Switzerland or death. Limited liability begins with the acquisition of taxable items in Switzerland and ends with their disappearance.
What is the tax liability of spouses?
Are life insurance policies subject to wealth tax?
How are the assets of minor children treated for tax purposes?
The wealth of minor children is generally added to that of their parents or the person with parental authority until they reach the age of majority, when they begin to be taxed individually on their personal wealth.
How are debts treated when calculating wealth tax?
Established debts are deductible from the total value of assets to determine taxable net wealth. This includes mortgages, personal loans and other documented debts.







