The Swiss Pension System
In Switzerland, the pension system is divided into 3 pillarswhich allow retirees to keep a equivalent standard of living or at least similar to the one he had while working.
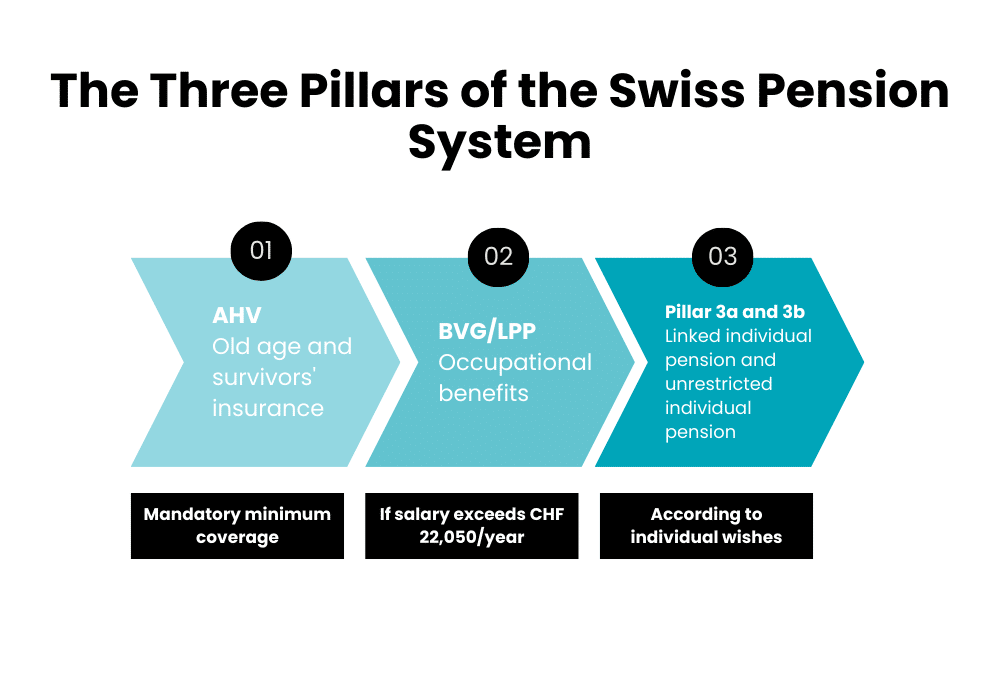
The 1st Pillar
The 1st pillar, known by the abbreviation AVS (Assurance Vieillesse et Survivants), is compulsory. Every Swiss worker contributes to the AVS until the age of 65.for both men and women.
The 2nd Pillar
The 2nd pillar, also known as BVG (Occupational Pensions Act) is added to the 1st pillar to top it up. Contributions are then shared ; you and your employer ; you both contribute together to build up your 2nd pillar. BVG/LPP is only compulsory for salaries in excess of CHF 22,050 per year.
The 3rd Pillar
The 3nd pillar is optional. It consists of tied personal pension plans (Pillar 3a) and unrestricted personal pension plans (Pillar 3b). It's up to each worker to feed it according to his or her desires and means. These two pillars each have their advantages and disadvantages.
Pillar 3a
This pillar is advantageous from from a tax point of view because you can deduct your contributions from your tax return. However, you should also bear in mind that contributions to this pillar are limited. You can contribute a maximum of 7056 CHF every year if you are an employee. If you are self-employed without 2nd pillar, you are also limited to 3CHF 5,280 per year.
Please note that if you wish to withdraw your 3nd pillar, you will have to pay tax on what you have contributed over the years.
Pillar 3b
Pillar 3b, on the other hand, is not limited like pillar 3a, but often does not generate the same income as pillar 3a. no tax benefits. Unlike Pillar 3a, if you decide to withdraw it, you won't have to pay tax.
Retiring at Normal Retirement Age
In Switzerland, if you want to retire at ordinary age (65)However, you shouldn't wait until you reach that age to apply for your various pensions. For all pillars, you'll need to make an application. at least three months before your 65th birthday.
To receive your 1st pillar, you will need to send a written request to the compensation fund to which you have paid AHV contributions throughout your working life.
To request your 2nd pillar, you will also need to send a request to your pension fund. They will then tell you what you need to do to receive your BVG pension, and how much you should expect to receive.
To request your 3nd pillar, you will need to contact the organization with which you contracted your pillar.
Early Retirement
Since 1st january 2024you can receive part or all of your 1st and 2nd pillars, before you turn 65. This is possible from the age of 63, or even earlier in some cases.
If you are a woman born between 1961 and 1969there will be other consequences. If you are affected by these dates and do not apply for early retirement, you will receive an additional pension. for life. If, however, you decide to anticipate the latter, your pension will be less reduced, for the rest of your life.
In any case, such a decision needs to be carefully thought out, as it may result in a shortfall in income, since early retirement reduces the 1st and 2nd pillar. We strongly recommend draw up a budget taking your situation into account. Once you've made your decision, you'll need to contact your compensation fund, which will present you with your options.
Both men and women can leave the workforce age 63 at the earliest and no later than age 70.
Retiring after Ordinary Retirement Age
If you wish to continue working over 65You can postpone your retirement for up to five years. It is also possible to continue working while receiving part or all of your 1st pillar.
AVS Stabilization (AVS 21 reform)
As a result of Switzerland's growing ageing population, the government has introduced AVS reform. To finance this reform, the retirement age for women was increased from from 64 to 65 yearsThe aim of this reform was to maintain This reform had a very specific aim, which was to maintain the current level of AHV pensions and to stabilize until 2030.
Conclusion
To help you prepare for retirement, there are a number of things you can do several options to determine which one is right for you, based on your specific needs. personal situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the retirement age for women?
Since January 2024, the retirement age for women has been the same as for men, i.e. 65.
What is the 3rd pillar?
It's an optional pillar, which is funded according to your wishes.
What are the consequences of the AVS 21 reform?
The retirement age for women has been raised from 64 to 65. It is also now more flexible. It is now possible to retire between the ages of 63 and 70, subject to certain conditions.
How and when to take early retirement
You will need to contact your compensation fund. Other conditions apply if you were born between 1961 and 1969.
Who do I contact to receive my annuities?
You will need to contact your compensation fund or the organization where you took out your 3nd pillar, if you have taken one out.
Sources
[1]“Effectif et Évolution de La Population En Suisse En 2021: Résultats Définitifs | Communiqué de Presse.” Office Fédéral de La StatistiqueAug. 25, 2022, www.bfs.admin.ch/asset/fr/23145951#:~:text=En Suisse200.







